Linear halogen light bulbs are efficient lighting devices that utilize tungsten filament technology. They are encased in a durable quartz envelope to withstand high temperatures. The halogen cycle enhances lamp longevity by recycling evaporated tungsten back onto the filament, preventing blackening and maintaining brightness. Although they provide superior light quality and an extended lifespan of up to 4,000 hours, they also convert around 90% of energy into heat, posing safety concerns. Further details about their functionality can be explored.
Key Takeaways
- Linear halogen light bulbs use tungsten filament technology encased in a durable quartz envelope for high-temperature resistance.
- They operate utilizing a halogen cycle that prevents blackening and enhances filament longevity by redepositing evaporated tungsten.
- The bulbs provide superior light quality with excellent color rendering, suitable for various applications.
- While efficient, about 90% of energy is converted to heat, leading to burn hazards and frequent replacements.
- Disposal can be challenging due to hazardous materials, prompting regulatory considerations in many regions.
Understanding Linear Halogen Light Bulbs
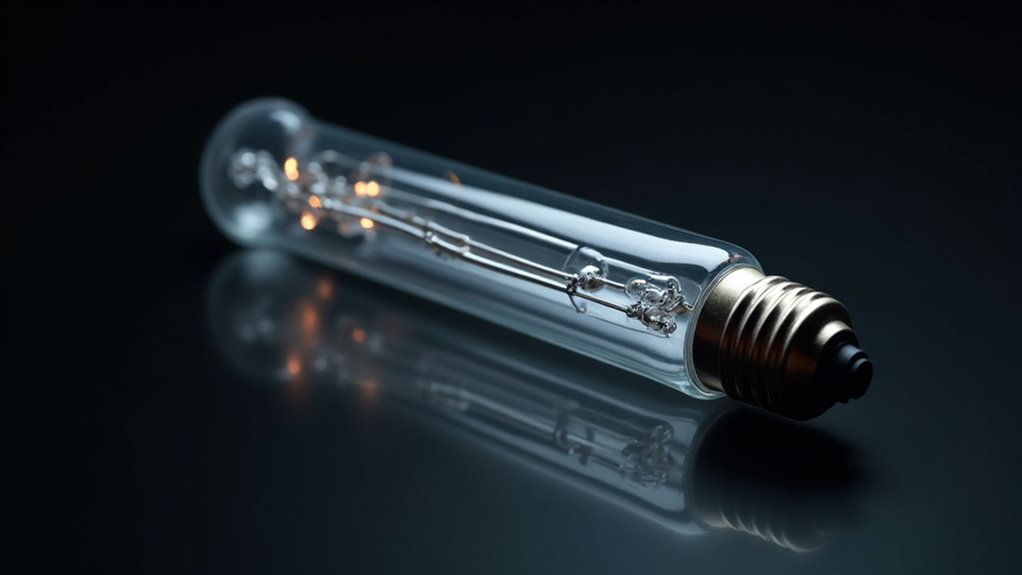

Understanding linear halogen light bulbs requires an appreciation of their unique construction and operational characteristics.
These incandescent lamps utilize tungsten filament technology, encased in a cylindrical quartz envelope that withstands higher temperatures than traditional glass. The envelope is filled with inert gas and a small quantity of halogen, which enhances their filament life and longevity. This technology allows for energy-efficient halogen bulbs that offer a brighter light while consuming less power.
Incandescent lamps feature tungsten filaments in durable quartz envelopes, enhanced by halogen for greater efficiency and longer lifespan.
Historically, this design marks an evolution in light bulb technology, offering a distinct narrow tubular shape, typically featuring double-ended R7s cap connectors. Common lengths vary, with standard sizes at 78mm and 118mm.
The filament is fully supported within the envelope, facilitating optimal heat distribution. While these bulbs produce bright, high-quality light with excellent color rendering, their design necessitates careful handling to maintain performance and lifespan.
The Halogen Cycle: How It Works
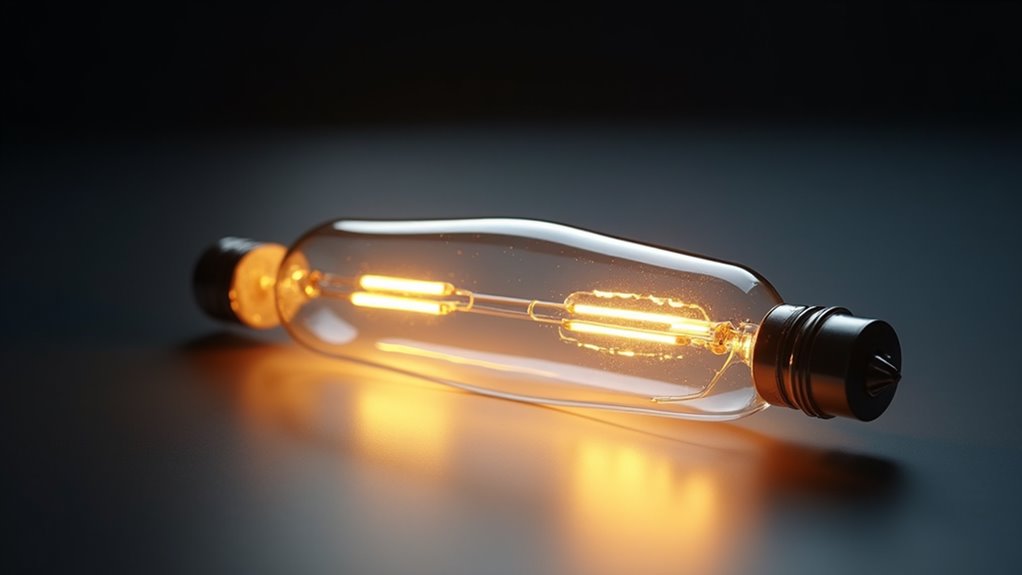

The halogen cycle begins with the tungsten filament reaching high temperatures, causing tungsten atoms to evaporate into the gas-filled envelope.
The evaporated tungsten then reacts with halogen gas, forming tungsten halide compounds that circulate within the lamp.
This chemical reaction is essential for maintaining filament integrity and preventing blackening of the bulb.
Tungsten Evaporation Process
A crucial process in the operation of halogen light bulbs is the tungsten evaporation process, commonly referred to as the halogen cycle. This cycle significantly enhances lamp efficiency and filament durability. The tungsten properties, particularly its high melting point, allow it to function effectively despite high temperatures.
Key aspects of the tungsten evaporation process include:
- The filament operates between 2500°C and 3000°C, inducing tungsten evaporation.
- In standard bulbs, evaporated tungsten contributes to bulb blackening, decreasing light output.
- The addition of halogen gas creates a reversible reaction, preventing tungsten deposition on the bulb walls.
- Tungsten halide molecules facilitate the redeposition of tungsten back onto the filament, enhancing its longevity and maintaining brightness throughout its lifespan.
Gas Reaction Mechanism
How does the halogen cycle enhance the efficiency of linear halogen light bulbs?
The halogen cycle facilitates gas interactions necessary for maintaining brightness and prolonging filament life. As the tungsten filament reaches high temperatures, tungsten atoms evaporate and react with halogen gas within the quartz envelope.
This reaction forms tungsten halides, which circulate through the bulb due to thermal dynamics and convection currents in the fill gas. When these compounds approach the heated filament, they dissociate, redepositing tungsten back onto the filament.
The freed halogen atoms are then available to engage in further reactions, renewing the cycle. This continuous regeneration prevents tungsten deposition on the quartz, ensuring consistent light output and enhancing overall operational efficiency.
Key Components of Linear Halogen Bulbs
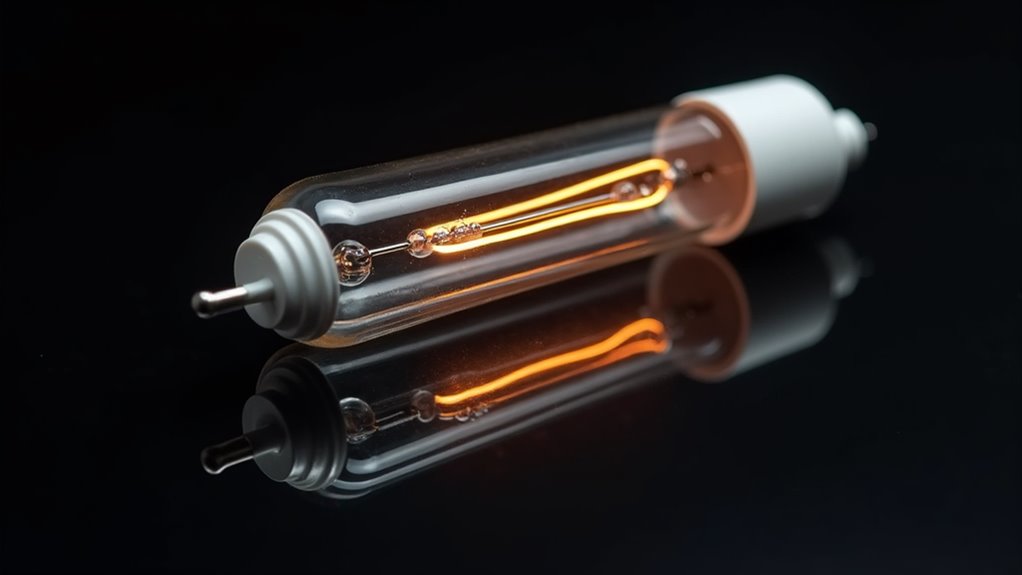

Key components of linear halogen bulbs include the quartz-glass envelope, tungsten filament, halogen gas fill, R7s ceramic end caps, and support wires. These components work in unison, employing advanced filament technology and precise gas composition to optimize performance.
- Quartz-Glass Envelope: Provides high-temperature resistance, containing gases and filament.
- Tungsten Filament: Coiled wire that incandesces under electrical current, with regeneration enabled by halogen gas.
- Halogen Gas Fill: Comprising an inert gas and halogen, it prevents tungsten deposits on the envelope, enhancing longevity.
- R7s Ceramic End Caps: Ensure electrical connection and fixture stability, designed to withstand extreme heat.
Together, these components facilitate efficient light production while maintaining structural integrity and extending the lifespan of the bulb.
Advantages of Linear Halogen Lighting
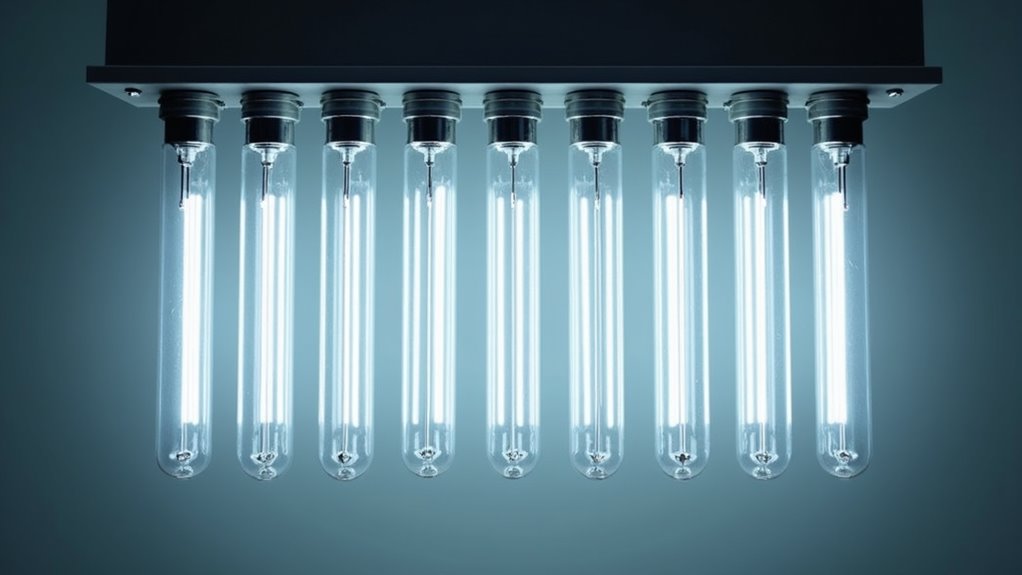

While many lighting options are available, linear halogen lighting stands out due to its exceptional performance characteristics and versatility across various applications. The advantages include superior light quality, enhanced lifespan compared to incandescent bulbs, and energy savings. Linear halogen bulbs typically last between 2,000 to 4,000 hours, benefiting from the halogen cycle that extends bulb lifespan. Additionally, they deliver a bright, white light with a high Color Rendering Index (CRI), ensuring colors appear vibrant.
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Superior Light Quality | Bright, clear light with excellent color rendering. |
| Enhanced Lifespan | Lasts longer than incandescent counterparts. |
| Energy Savings | Improved efficiency with reduced energy consumption. |
| Versatile Applications | Suitable for diverse settings and purposes. |
Disadvantages and Considerations

Although linear halogen light bulbs offer numerous benefits, several disadvantages and considerations warrant attention when evaluating their use.
- Energy Waste: Linear halogen bulbs convert approximately 90% of energy into heat rather than light, leading to higher electricity bills and an increased carbon footprint.
- Burn Hazards: Operating at high temperatures creates risks of burns and fire, especially if positioned near combustible materials.
- Maintenance Costs: With lifespans averaging 1,000 to 2,500 hours, they require frequent replacements, resulting in elevated maintenance costs.
- Environmental Impact: They contain hazardous materials and are not easily recyclable, complicating disposal and contributing to regulatory phase-outs in various regions.
These factors must be carefully considered against the advantages when selecting linear halogen lighting.
Common Applications for Linear Halogen Bulbs
Linear halogen light bulbs, due to their intense brightness and versatility, find application across various settings.
In outdoor applications, these bulbs are frequently used in floodlights and security lighting fixtures, providing essential illumination and deterring intruders.
For residential uses, they serve in uplighters, floor lamps, and are integrated into ceiling and wall luminaires, enabling adjustable mood lighting.
In commercial settings, linear halogen bulbs highlight product displays in retail environments and provide safety lighting in warehouses and factories.
Additionally, these bulbs excel in specialty lighting, such as heat lamps for food service and in theatrical lighting due to their compact size and high Color Rendering Index.
Their broad applicability underscores their importance in diverse illumination requirements.



Bài viết cùng chủ đề:
Top 5 Security Flood Light Bulbs for Protecting Your Home
Choosing Title 20 Compliant Light Bulbs for Your Home
Top 3 LED Office Light Bulbs for Bright Workspaces
Top 5 PAR 20 LED Light Bulbs for Home Lighting
5 Best Battery-Operated LED Picture Lights for Artwork in 2025